When a client visits some website, he/she tries to solve a certain task. So, there should not be any additional problems for him/her, such as difficult and confusing navigation, which badly displays the information provided on the portal.
If a web page has a certain confusion in the simplest places (for example, blocks and elements that are easy to perceive are displayed incorrectly), the user most likely won’t find a solution to his/her task and will simply go to another web resource. There’s a high competition among websites in modern online communities, which means that when one creates and tests new software, he/she must comply with all regulations and quality standards.
Usability testing – is a specific procedure that helps study the level of user learnability while interacting with the developed software. Such a kind of testing is considered as the most important thing of any Internet marketing.
The final goal of any usability testing is to understand, even at the software development stage, whether the clients, whom the web product is created for, can independently make sense of the provided interface and how quickly they will do it.A user-friendly website allows you to increase significantly the number of people who will become its users for a short or long period of time.
And the more customers there are, the higher the conversion of the website is (the percentage ratio of the number of customers who performed certain actions on the website to the total number of visitors for the selected time period). Clients always get maximum pleasure while interacting with properly configured and organized site content.
But when web designers are busy creating a prototype of the future site, they cannot objectively assess the future convenience of its usage due to certain personal qualities and direct participation in its creation. The layout of the site that they develop will always seem to them as convenient and understandable as possible.
Therefore, most of the inconveniences and errors appear at the stage of designing. Then, experts from the QA department are assigned to the project, and their main task is to test the software from the end user side.
Features of Usability Testing
The usability testing is executed in a form of so-called “black box” and “white box” testing. QA specialists become simple users from some product audience for a while, they try to study its features as much as possible with the subsequent forming of their personal conclusion.
During testing on the basis of the white box method, the main thing is to study the current level of satisfaction while the user is interacting with additional systems, parameters and system modules which are presented on the site. The initial creation of a correct and convenient system interface will increase the speed of creating the program code, and will also have a positive effect on the quality of the final product in general.
You should take into account the fact that the usability testing needs to be executed at all stages of web product testing (starting from the stage of unit testing and during the acceptance and system tests). Also, it is necessary to use sets of test cases for different types of clients at every stage: from a thoughtful developer to an average user.
So, at first, we’ll highlight the most common errors during usability testing of the sites.
Web Site Usability Errors
- An excess or lack of data on the portal;
- The structure of web pages is maximally overloaded with graphical content;
- Incorrect location of the most requested functional units;
- Incorrectly configured grouping of products or services;
- A complete absence of clear instructions or explanations of how to use the provided site functionality;
- Difficult or inconvenient navigation on the website pages.
Common requirements and standards for usability testing of the sites were created gradually from these and similar errors. Testing and analyzing the site usability, the process of finding defects, the bug fixing and the ongoing improvement can significantly increase the general conversion of the site.
All this can be done if you take into consideration the basic factors that directly affect the current usability.
- Navigation block. It is recommended to minimize the number of users’ moves on a site, to build an intuitive and convenient structure of working with the website functionality.
- Design. You must adhere to the same style and the palette in the design of the site pages;
- Work with pages of advertised content (goods or services). Cards of products or services should be filled with the most comprehensive information, contain high-quality images and/or video materials;
- Minimized ordering procedure. The form for ordering a product or service must contain the minimum number of required fields to fill in;
- Searchability. Competent search with the opportunity to easily filter by a category, section and price – a good advantage in order to increase conversions;
- Fast page loading. The greater the speed is, the better;
- The relevance and quality of the posted content. The main thing is not just the authenticity of the texts, but also their number, as well as the regularity of such blocks updating.
The aspect of evaluating the convenience of interacting with the website is very important too. Today this is one of the most essential moments while interacting with the users’ behavioral factors on the Internet.
It will be easier and more pleasant for the client to interact with those sites that correspond to all current rules and standards of usability. Such a portal will be intuitive, easy to use, and accordingly facilitate increasing the number of users and the level of search results, etc. All user factors are working to improve the site, gradually bringing the success to its owners.
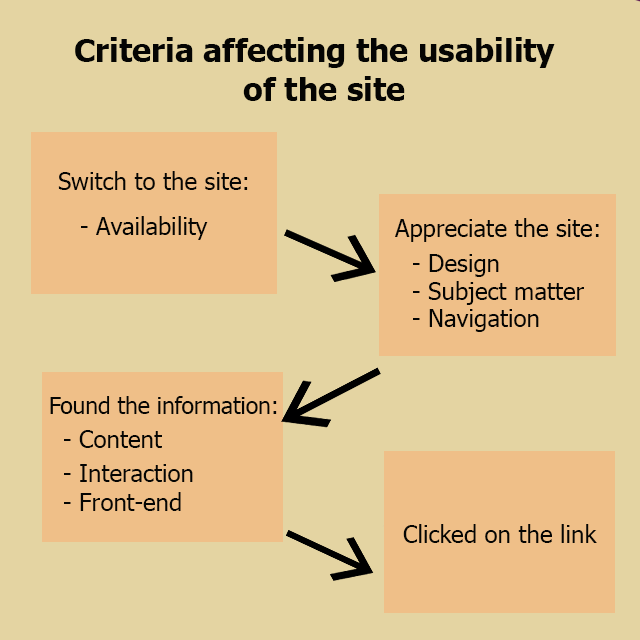
Criteria affecting the usability of the site
Current Assessments of the Website Usability
Nowadays the following criteria are applied when analyzing the convenience and comfort of interacting with websites:
- Easy to understand. How quickly will potential users be able to understand what needs to be done on the site to solve their task or problem? Does the site have a page or a block with information that provides such assistance?
- Intuitiveness. Is the graphical interface of the site readable? Does a user have the opportunity to understand where he/she needs to go in order to solve his/her questions and tasks?
- The productivity of use. How effectively customer issues are solved? Can this process be easier? How many steps does the client need to perform in order to solve his/her tasks? (and the fewer such steps are, the better);
- Errors in the interaction. What is the probability that the client will make a mistake while interacting with the functionality of the site, and what problems will this lead to?
- The level of tolerance towards errors. How quickly will the client understand exactly what his/her actions had led to mistakes and what he/she needs to do to fix them?
- Potential. Do all the elements and blocks that were designed to solve a client problem work according to a correctly defined logic?
- Page performance. How quickly are the pages loaded?
- How quickly you can find the right information. Is the most important and relevant information on the main page or in the most visible navigation areas on secondary pages?
- Satisfaction with interaction. How does the client work with the system, how quickly can he/she solve all the questions, are there any moments and situations that cause certain aggression or irritation? Will he/she want to recommend this site to friends and relatives in the future?
The usability testing procedure is aimed at increasing the customer satisfaction from visiting website pages and the level of interaction easiness with product functionality. Any usability is based on such important aspects:
- Text content;
- Structuring and formatting of the text;
- Availability of functional blocks on the pages and the logic of their functioning;
- Logically correct arrangement of important elements on the pages towards each other;
- Simplification of customer interaction with the product due to certain navigation tips;
- The attractiveness of site design and so on.
This is a kind of summarizing list that developers should focus on when they create the most optimal product. In addition, at any stage of the work on the website, one should follow the common rules which help to make a convenient and attractive product that brings the maximum benefit to its owners.
The main recommendation: the simpler, the better. Also, the practice of classical solutions usage is particularly effective – clients get used to a certain group of algorithms, the visual arrangement of blocks and can easily understand the work of such logic on third-party portals.
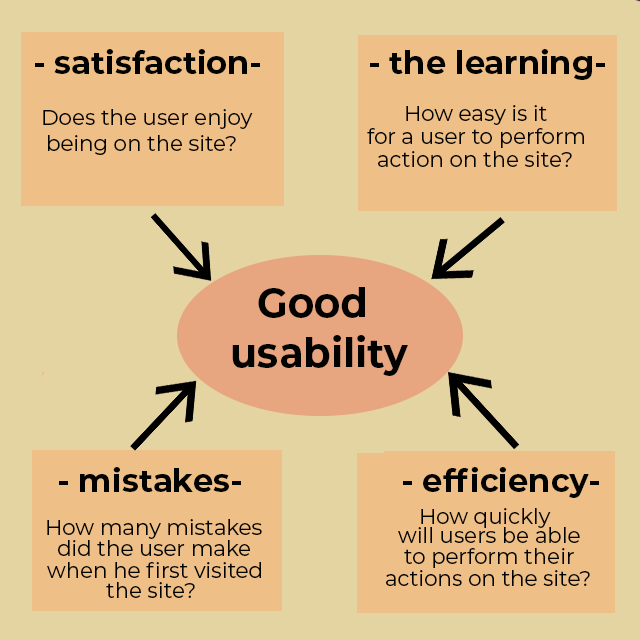
Good usability
Also, we can analyze the logic of testing input forms in more detail. Users will face such forms anyway when they are on sites that offer certain goods and/or services.
Examples of usability testing for correct form filling:
- All entered data is saved after input completion;
- The navigation panel shows a user a stage where he/she exactly is, what steps he/she has already completed, and what else he/she has to do to fill in the required fields;
- Blocks of hints and instructions contain only easy-to-understand information and can be correctly perceived by even the most inexperienced customers;
- If the initial names of the fields are not specified, they should be displayed immediately after the mouse cursor is on them;
- A group of required fields is marked with a specific symbol (for example, a special * sign). It will be good to display the reasons for the obligation to fill in certain fields;
- The client receives an email containing the confirmation that the form has been successfully completed, as well as information about the following usage of this form;
- During the authorization process, the personal data of the client is automatically entered into the form;
- The “Send” button will become active only when the user successfully completes all the required fields, and marks the “I accept the end-user license agreement” checkbox;
- If the client enters incorrect information, there’s a text message (in the case if that data has not passed the validation established on the site).
In the day-to-day work, QA specialists must solve issues related to simplifying user tasks, study in detail the logic of the developed product’s behavior in order to make the process of client interaction with software as simple and clear as possible. The procedure of any usability testing is the constant creating of clear and convenient resources which users will be pleased to interact with.










Leave A Comment